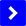
The detection light emitted from a point light source is focused onto the observed object through a lens. If the object is exactly at the focal point, the reflected light should converge back to the light source through the original lens. This is what is called confocal, or simply confocal.
The Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope(CLSM or LSCM) adds a dichroic mirror to the optical path of the reflected light, folding the reflected light that has passed through the lens in other directions. There is a Pinhole at its focus, and the small hole is located at the focus. Behind the baffle is a photomultiplier tube (PMT).
It can be imagined that the reflected light before and after the focal point of the detection light passing through this confocal system will surely not be focused onto the small hole and will be blocked by the baffle. So what the photometer measures is the intensity of the reflected light at the focus.
Its significance is: By moving the lens system, a three-dimensional scan of a semi-transparent object can be conducted.