In addition, the color temperature of the lighting source will affect the color rendering effect. For the same specimen, when the lighting color temperature is relatively low, the red in the specimen is more vivid and the blue is darker; on the contrary, when the color temperature is higher, the blue in the specimen is more vivid and darker.
There are two types of light sources commonly used for brightfield illumination in microscopes: halogen lamps and LED lamps.
The overall color temperature of the halogen lamp is relatively low, and it looks obviously yellowish. Generally, a daylight filter is added to the illumination light path to increase the color temperature and make the color of the specimen more balanced. However, the color temperature of the halogen lamp changes with the brightness of the lamp. The brighter the lamp is adjusted, the higher the color temperature. We know that when using a microscope to switch from a low-power objective to a high-power objective, the illuminating light needs to be brightened to ensure that the brightness of the visual field observed by the eyepiece is consistent. This will cause the color temperature to rise, thereby making the specimen seen by the high-power lens blue The structure is more vivid than in the low-power lens, and the red structure seen in the low-power lens is more vivid. To solve this color deviation, the methods are:
The basic microscope can be equipped with a constant-brightness objective lens group. The low-power lens has the same brightness as the high-power lens, so there is no need to adjust the brightness of the lamp.
Advanced fully automatic microscopes use a constant color temperature wheel to automatically adjust the brightness of the halogen lamp and automatically adjust the color temperature wheel according to different objectives to keep the final illumination color temperature constant.
Use a constant color temperature lighting source: LED lights.
The color temperature of the LED lamp is constant and does not change with the brightness. The color temperature of LED lamps for microscope brightfield illumination is usually constant at 5000K, which is close to the average color temperature of sunlight.
Finally, when using the camera equipped with the microscope to take pictures, if you find that the image displayed on the computer screen has a color shift, you need to do a white balance first.
The vividness of the color can be adjusted by the color saturation. The higher the saturation, the brighter the image color. When the saturation is the lowest, the image loses its color and appears as black and white.
Phase-contrast imaging
When checking the growth status of living cells in culture, the phase difference method is commonly used to observe. Because living cells are generally not stained and the cells are relatively transparent, it is not easy to see clearly if you observe directly in the bright field. The contrast can be improved by using the phase-contrast method (The figure below), and it is easier to see the cell status.
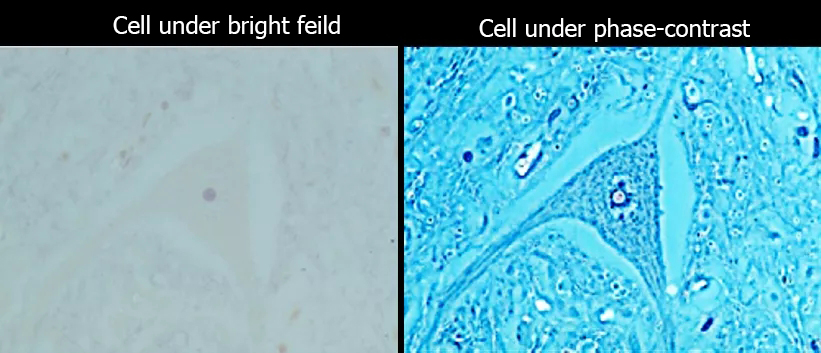
The microscope needs two conditions to achieve the phase difference effect: phase difference objective lens and phase difference ring. During the observation, you need to select the phase difference objective lens and move the corresponding phase difference ring into the optical path. There will be marks "PH0", "PH1", "PH2", etc. on the phase difference objective lens. The numbers indicate the corresponding phase difference ring model. In addition, the corresponding objective lens multiples will be clearly marked on the phase difference ring. When using the phase difference, be sure to ensure the objective lens and the phase difference ring match correctly.
The information is provided by optic illuminator manufacturer.